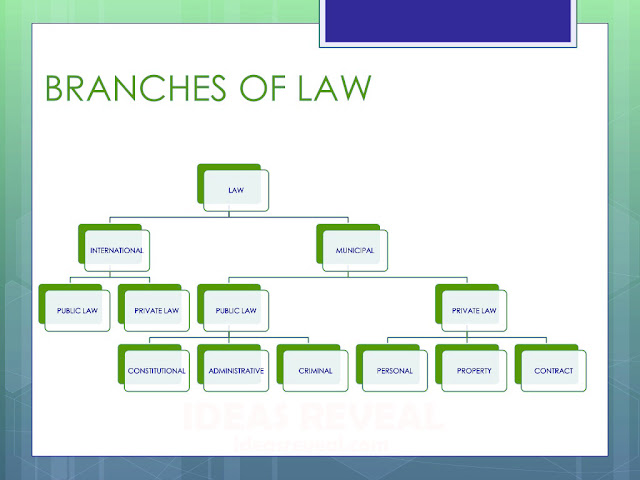
The main branches of law are:
·
Criminal
Law
·
Civil
Law
·
Contract
Law
·
Tort
Law
·
Property
Law
·
International
Law
·
Constitutional
Law
·
Administrative
Law
·
Labor
Law
·
Environmental
Law.
Criminal
Law
Criminal law is a branch of law that deals
with crimes and criminal behavior, including the prosecution of individuals and
organizations charged with criminal offenses and the punishment of convicted
offenders. It sets out the definitions of various crimes, such as murder,
theft, and fraud, and specifies the penalties for each. The primary aim of
criminal law is to protect society and maintain order by punishing and
deterring criminal behavior.
Civil Law
Civil law is a branch of law that deals with
disputes between individuals or organizations, such as contracts, torts, and
property rights. It aims to provide a legal remedy for harm suffered by one
party as a result of the actions of another, and to enforce the rights and
obligations of parties under civil law. Civil law is generally distinct from
criminal law, which deals with offenses against the state, although there can
be overlap between the two. Civil law is often resolved through a court trial
or arbitration, with a judge or arbitrator determining the outcome and awarding
compensation or other remedies.
Contract Law
Contract law is a branch of civil law that
deals with agreements between parties to do, or refrain from doing, certain
things. A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties,
and contract law governs the formation, performance, and enforcement of
contracts. Contract law sets out the requirements for a valid contract, such as
offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual assent, as well as the rights and
obligations of the parties under the contract. If one party breaches the
contract, the other party may be entitled to damages or other remedies, such as
termination of the contract. Contract law is central to commercial transactions
and is widely used in business and consumer transactions.
Tort Law
Tort law is a branch of civil law that deals
with wrongs committed against individuals or organizations, for which the
injured party may be entitled to compensation. A tort is a civil wrong that is
committed by one person against another, such as negligence, intentional harm,
or strict liability. Tort law sets out the legal rules for determining whether
a tort has been committed, and the remedies available to the injured party.
Remedies in tort law can include compensation for damages, such as medical
expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering, as well as injunctive relief,
such as an order to stop an ongoing harm. The primary aim of tort law is to
provide a remedy for harm suffered by individuals or organizations and to deter
harmful behavior.
Property Law
Property law is a branch of civil law that
deals with the ownership, use, and transfer of property, including real
property (land and buildings) and personal property (tangible and intangible
assets). Property law governs the rights of individuals and organizations to
own, use, and dispose of property, as well as the rights of others with respect
to that property. Property law sets out the legal rules for acquiring, holding,
and transferring property, including the rules for conveying title, creating
and enforcing liens, and resolving disputes over property ownership and use.
Property law is an important aspect of many commercial transactions, and it
plays a central role in the development of real estate, finance, and other
industries.
International
Law
International law is a branch of law that
governs relations between nations and other international actors, such as
international organizations and individuals. It sets out the rules and
principles that govern interactions between states, including the settlement of
disputes, the protection of human rights, and the regulation of trade,
investment, and other forms of cross-border cooperation. International law is
based on treaties, customary law, and general principles of law, and it is
enforced through a range of mechanisms, including diplomacy, negotiation, and
international courts and tribunals. International law is a crucial aspect of
the international system and plays an important role in maintaining peace,
security, and stability among nations.
Administrative Law
Administrative law is a branch of law that
deals with the powers, duties, and procedures of government agencies and other
administrative bodies. It governs the creation, operation, and oversight of
these bodies, and sets out the legal rules for their decision-making,
rulemaking, and enforcement activities. Administrative law also provides for
judicial review of administrative actions, enabling individuals and
organizations to challenge decisions made by administrative bodies that affect
their rights and interests. The primary aim of administrative law is to ensure
that government agencies and other administrative bodies act within their
authority and in accordance with due process, and to provide a mechanism for
resolving disputes between individuals and organizations and the administrative
state.
Labor Law
Labor law is a branch of law that deals with
the rights and obligations of workers and employers in the workplace. It
governs the terms and conditions of employment, including wages, hours of work,
health and safety, and discrimination. Labor law sets out the legal rules for
the formation and operation of labor unions, and governs the collective
bargaining process between unions and employers. It also provides for the
resolution of labor disputes through mechanisms such as strikes, lockouts, and
arbitration. The primary aim of labor law is to protect the rights of workers
and to ensure that employers adhere to fair labor practices, and to balance the
interests of workers and employers in the workplace.
Environmental Law
Environmental law is a branch of law that
deals with the protection of the natural environment, including air, water, and
soil, as well as wildlife and other natural resources. It sets out the legal
rules for preserving and conserving the environment, and for preventing and
mitigating harm to the environment. Environmental law covers a wide range of
issues, including pollution control, hazardous waste management, conservation
of natural resources, and protection of endangered species. Environmental law
is enforced through a combination of federal, state, and local laws, as well as
international treaties. The primary aim of environmental law is to promote
sustainable development and to protect the natural environment for present and
future generations.





0 Comments